
Professor Joubert commenced research in molecular and cellular cancer physiology at the University of Pretoria (UP) in 1998 when she was appointed as a senior technical assistant in the Department of Physiology after obtaining a PhD in Biochemistry (UP).
Through her work, she hopes to strengthen collaborations with industry, and national and international research collaborations with the University of Oxford (UK), University of Bath (UK), University of Florida (USA), Baylor College of Medicine (USA), CRI INSERM (France), Joseph Fourier University (France) and Sabanci University (Turkey).
The focus of Prof Joubert’s research is mainly breast cancer, which is one of the most common forms of the disease in women – the lifetime risk of South African women getting breast cancer is one in 27. Her research focuses specifically on:
a) the in silico design performed by computer simulation of potential anti-cancer agents;
b) the chemical synthesis thereof in liaison with a pharmaceutical company; and
c) the evaluation of these agents for improved anti-cancer treatment.
The prevalence of cancer is increasing worldwide. Globally, 14 million people are diagnosed with the disease each year, and about nine million lose their lives to it annually. According to the Cancer Association of South Africa, breast cancer in women and prostate cancer in men are among the top five cancers prevalent in the country. However, according to the World Health Organisation, between 30 and 50% of all cancer cases are preventable.
The research findings of Prof Joubert’s group contribute to the use of in silico virtual screening (VS) methods to identify lead compounds that are likely to succeed in further downstream assays and screens, including whole genome microarrays as well as protein arrays, in the search for potential anti-cancer agents. Making use of in silico VS methods helps scientists to identify novel compounds that significantly lower the cost of drug development by negating the need to synthesise unnecessary compounds that could not be removed prior to screening.
Prof Joubert is also contributing to translational research that entails scientific discoveries that can be applied to improve health outcomes and health care in the Faculty of Health Sciences and the Faculty of Natural and Agricultural Sciences at UP, thus addressing the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal 3 (Good Health and Well-being).
She recently commenced with a leukaemia research project that looks at the role of platelets in the progression of chronic myeloid leukaemia, a condition that affects mostly older adults and is a type of leukaemia of the haematopoietic stem cells. Her fundamental cancer research links with clinical research, further contributing to translational research with a specific benefit for South African and African populations with unique genotypic and phenotypic characteristics.
Prof Joubert’s research efforts were prompted by the passing of her father, after he was diagnosed with chronic myeloid leukaemia in September 2020 and COVID-19. She says that he taught her to believe in herself and to do her part to improve the quality of life of the people that she interacts with every day. Her other role models are Prof Albert Neitz, who supervised her PhD degree, and Prof Dirk van Papendorp, Head of the Department of Physiology. Both academics inspired her and motivated her to go the extra mile in her career, Prof Joubert says.
Keeping in mind the life skills her father taught her, Prof Joubert dreams of touching lives and hopes to be regarded as a good mentor to students and colleagues. “I would like to be remembered for having contributed to someone’s life in a positive way, whether it is teaching undergraduates and postgraduates, or contributing to the good health and well-being of all people.”
For relaxation, she enjoys pilates and gardening.
 Talking Point
Talking Point
Researchers at the University of Pretoria (UP) have been working to identify genes that make African women more susceptible to certain forms of breast cancer. However, this is no easy task as very little genomic information is known about African populations.
 Story
Story
Researchers at the University of Pretoria (UP) are making today matter by battling aggressive breast cancer through identifying genes that make African women more susceptible to certain forms of breast cancer. However, this is no easy task as very little genomic information is known about African populations. This is just one of UP's research projects that aim to ensure that there is a clear...
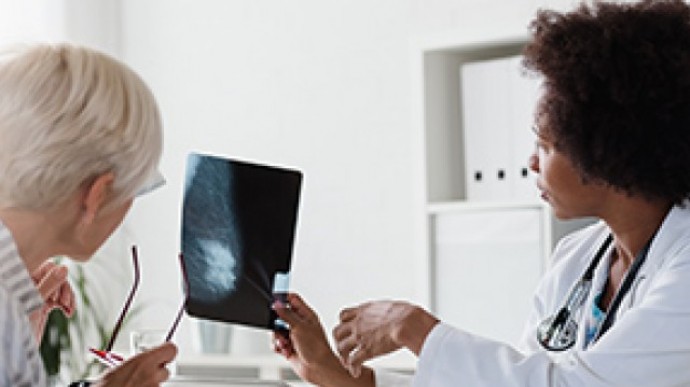 Talking Point
Talking Point
Globally, 14 million people are diagnosed with cancer each year, and about nine million lose their lives to the disease annually. But next-generation DNA technologies and sequencing are heralding a change to the outlook of the disease, and the rapid development and roll-out of DNA tests could save lives.
 Story
Story
October is Breast Cancer Awareness Month, an annual campaign by private and public healthcare organisations to increase awareness of the disease on a national scale. In the infographic below, UP researcher Professor Annie Joubert guides us through some fast facts on breast cancer and what you need to know about the disease.
 Infographic
Infographic
October is Breast Cancer Awareness Month, an annual campaign by private and public healthcare organisations to increase awareness of the disease on a national scale. In the infographic below, UP researcher Professor Annie Joubert guides us through some fast facts on breast cancer and what you need to know about the disease.
 Talking Point
Talking Point
It’s estimated that about 7% of all breast cancer cases diagnosed occur in women under the age of 40. According to the American Cancer Society, about one in eight invasive breast cancers develop in women younger than 45, whereas two in three invasive breast cancers occur in women aged 55 or older. Breast cancer occurrence also differs between patients diagnosed before and after menopause.
Copyright © University of Pretoria 2025. All rights reserved.
Get Social With Us
Download the UP Mobile App